Studying The Difference Between Vector And Raster Images
Table of Contents
- What Are Vector Images?
- What Are Raster Images?
- The Difference Between Vector And Raster Images?
- When To Use Which: Vector And Raster Images
The world of digital design and photography is vast and proliferating. As a newbie designer, marketer, or web developer, you may be confused with the plethora of file types, sizes, and dimensions. If you are looking for the correct way to navigate them all, it is crucial first to understand the difference between vector and raster images. Why so?
You will encounter raster and vector images regularly if you work with digital photos, logos, and graphic designs. These are the two most common files used in design, photography, and illustration. Vector and raster images decide your every step of work, right from choosing the software to producing accurate designs.
So, let’s find out more about vector and raster images.
What Are Vector Images?
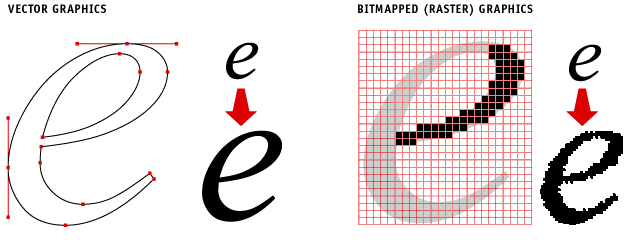
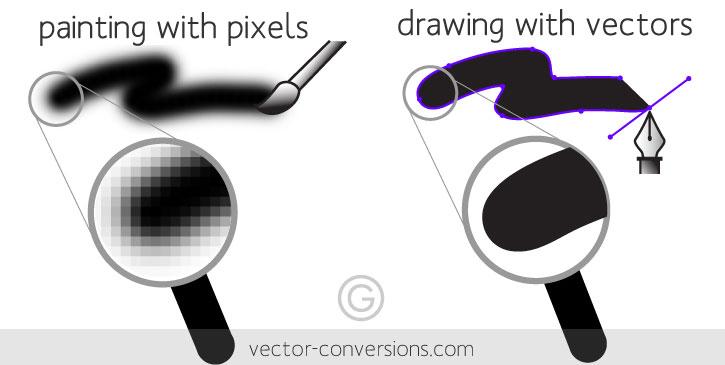
Imagine you are playing connect the dot, where one dot leads to another, and then another, and as you connect them, you form an image. This is more or less how vector images work. Anchored dots are connected by lines and curves, resulting in scalable vector graphics or, in short, SVG files.
Thus, vector images are composed of lines, curves, and points (anchors), all mapped out on a grid. Naturally, vector files do not have any pixels. Instead, they use mathematical equations to capture the shape, border, and color that build an image. Here, lines, curves, and other elements are paths, whereas the formula is a vector. The formula tells the path how it is shaped, what color it is filled with, and what the borders are like.
You can scale a vector image up and down using any vector-based software. The mathematical formula recalibrates to the new size you give the file, so it is possible to maintain the same image quality across various dimensions. This also means that a vector file can be scaled infinitely. To create and edit a vector image, you can use Adobe Illustrator and CorelDraw programs.
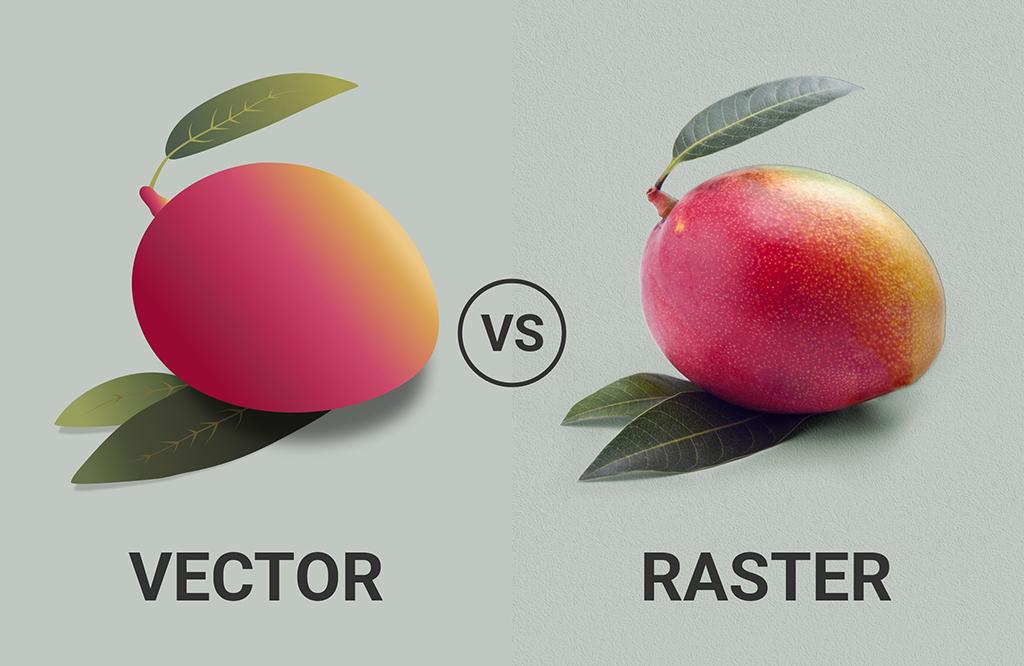
Given below is an example of a vector image. As you can see, each point is defined, color gradients are smooth and even, and the lines, dots, and curves are all neat and precise. Vector images are composed of shapes wherein each shape has its own solid color.

What Are Raster Images?
Hundreds of thousands of tiny colored squares arranged side by side makes a raster file. Raster images are made of pixels arranged precisely to procure detailed and high-quality photos. Raster files are also known as bitmaps.
To break it down further, pixels are just minute square-shaped dots that use color and tone to make an image. And while a single pixel may appear as just a blob of color, many pixels can come together to create complex, multi-colored images. An excellent quality raster image can contain up to millions of pixels. Raster images are hence capable of showcasing soft color gradients, a feature that is not present in vector images.
The most common example of a raster file is a digital photo you take on your phone camera or DSLR. All the images you see in print are raster images, too. The most common file types for raster images are JPEG, GIF, and PNG.

How raster images are used depends upon the quality and size of any image. Each file can contain only a set number of pixels. The number of pixels decides the size of the image, also known as the resolution. The more pixels an image has, the higher it will be in detail and quality. And as the number of pixels goes down, so does the sharpness and detail of a raster image.
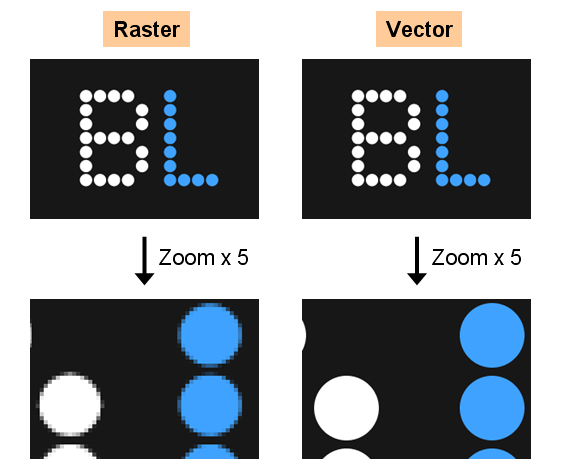
With this limitation in resolution, the size to which a raster image can be scaled up also gets limited. For example, if you try to scale up a picture with fewer pixels, it will result in a blurred image. Whereas, if you print a high-res image in a small size, the pixels will cram together. This will result in a distorted image.
The Difference Between Vector And Raster Images
- Resolution and scalability
The primary difference between raster and vector images is their resolution. Raster files are measured in DPI, i.e., dots per inch, or PPI, i.e., pixels per inch. A high-resolution raster image will showcase a variety of colors, resulting in excellent color editing. Such images also show better light and shading. However, when raster images are resized, they lose their quality.
On the other hand, vector images work on mathematical calculations. You can hence resize, rescale, or even reshape a vector image without compromising on its quality.

- Usage
Raster files are used in digital photographs. Any screenshot of a screen, pictures from digital devices, and online JPEGs are all raster images. Due to the level of detail, color, and grading raster images can provide, they are used for printing high-quality images. Raster files are thus used on billboards, flexes, and large posters.
Vector images are better suited for digital illustrations, such as logos, graphic designs, and animations. And since scalability is not an issue with vector files, they are also suitable for certain types of print formats.
- File types and sizes.
Because they use many pixels, raster images are usually larger than vector images. As a result, such files take up a vast amount of storage space on your device or slow downloading speeds on your website. On the other hand, vector files take up less storage space because stored math formulas determine their design.
The most common file types for raster images are JPEG, GIF, and PNG. In contrast, vector files are EPS, SVG, and AI files.
When To Use Which: Vector And Raster Images
Vector files are small in size and highly scalable. This makes them a friendly tool for printing marketing collateral. So, if you are printing business cards or flyers, designing an e-invite, or working with a cute illustration, vector images will serve your purpose.
Digitally, vector files are used in the lower thirds for videos, 2D and 3D animation, and web-based objects. Other uses of vector images include making coin designs, engraving on laser, printing on t-shirts, etc.
Raster images are suited for digital photos and large, high-definition prints. Below, the image breaks down the look of pixels and vectors when you zoom into their respective images.

To Summarize
With clarity on raster and vector differences, you are all set to experiment with your photos, designs, and illustrations using the correct methods. Read the frequently asked questions on vector and raster images below to learn more about the subject.
Key Takeaways
- Both vector and raster images play a pivotal role in photography and design. They cannot be used interchangeably, which gives both the file types a unique purpose and usage.
- Raster and vector differences may prevail, but they are also used together. Brochures, flyers, and posters are common examples. These templates use vector graphics (company logo, mascot, etc.), raster images, and text together.
- More software work with raster images than vectors. And while raster files are more versatile, in many cases, vector images prove better in usage. It is thus essential to understand the difference between raster and vector graphics and make an informed decision.
FAQs
An EPS file is a vector graphic of the Encapsulated Postscript format. EPS files store bitmap image information as well as text. Such files deal with scaling images that are high-res. At the same time, EPS files store a low-res version of the bitmap image, which helps preview the image.
In simpler words, EPS files are vector images designers use for high-quality, professional image prints. EPS files produce huge, detailed images, such as the ones you see on the road on a billboard. EPS files are also helpful for large posters, flex banners, and other marketing collaterals that require fine printing.
Yes, Adobe Photoshop is a raster-based program. Images are created on the platform using pixels, and hence Photoshop is widely used for working with digital photographs. However, designers often choose to open and edit vector files in Photoshop. Editing vectors on PS has limitations, as they can only be worked with as a smart object or a rasterized file.
Thus, if you are working with raster images, Photoshop can be an excellent tool to edit pictures and make photograph-based creatives.
The nature of a PDF file depends on the program used while creating the document. PDFs are mostly vector files, and only sometimes are they raster files. For example, a PDF created using Illustrator would be a vector file. However, a PDF created using Photoshop will get saved as a raster file.
JPEGs are the most common files used anywhere on the internet. They are photographs of some sort, which makes JPEGs raster images. JPEG stands for joint photographic experts group. It is a lossy format of raster images, and their size is denoted by the width and height of the image in pixels.
Yes, you can convert a JPEG file into a vector. The easiest way to do so is by using Adobe Illustrator. Open the program and select the option to start a new project. Insert the JPEG image you wish to convert, and select “Tracing” under “Window > Workspace.” Next, you can adjust the pixels and colors on the image to your liking. Then, save the file as a vector image. If you’re working on the file for usage on a website, save it as an SVG file. If you’re using vector images for printing, save the file as a PDF.
Latest Blogs
Explore how Google’s 2025 AI search updates triggered ranking chaos. Learn actionable strategies to adapt your SEO for AI Overviews, zero-click searches, and SERP volatility. Stay ahead now.
Learn how to rank on AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini by optimizing your content for authority, structure, and relevance. Stay ahead in AI-driven search with this strategic guide.
Explore the best healthcare SEO services for your medical practice. Improve online visibility and effectively reach more patients in need of your services.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Design
7 mins read
15 Best Firms Offering Design Services in India

Design
5 mins read
All You Need to Know About Data-Driven Design

Design
6 mins read