Table of Contents
- What Is Design Thinking?
- What Is the Purpose of Design Thinking?
- What Are the Benefits of Design Thinking?
- The Design Thinking Methodology in Action: An IBM Case Study
- How Can You Apply Design Thinking at Work?
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion
- FAQs
Design thinking has emerged as a new industry concept in recent years. And while this sounds like a complex idea, design thinking has proved its mettle as a world-changing force in the realm of business, especially after brands like Apple and Airbnb approved of its status as a notable idea.
It is now even a separate subject in the curriculum of leading international business colleges. We’re sure you must be grappling with the question, “What is design thinking?” Design thinking has become a popular industry catchphrase in the process of problem-solving. It is being applied as an innovative approach to several spheres, such as education, business, technology, marketing, and more. Let’s take a closer look at this creative problem-solving technique.
What Is Design Thinking?
Design thinking is too vast and nuanced to be explained in a limited number of words. It is an ideology and process at the same time. To phrase it better, design thinking is aimed at helping businesses and individuals solve complex problems in a highly user-centric manner.
It is an approach used for problem-solving that is practical as well as creative. While it sounds like it is closely associated with design, which it sure is, the inspiration behind the process can be tailed back to several sources, such as business, architecture, and even engineering.
Design thinking is an approach applicable to not just business but any field. It is highly user-centric and places extreme emphasis on the needs and problems of the users. Since it is a solution-based method, it then proceeds to find solutions to the users’ pain points.
While a problem-based thinking method focuses on obstacles and problems and often tends to fixate on them, a solution-based approach, such as design thinking, draws from the needs of the user and builds a constructive solution to effectively tackle that specific problem.

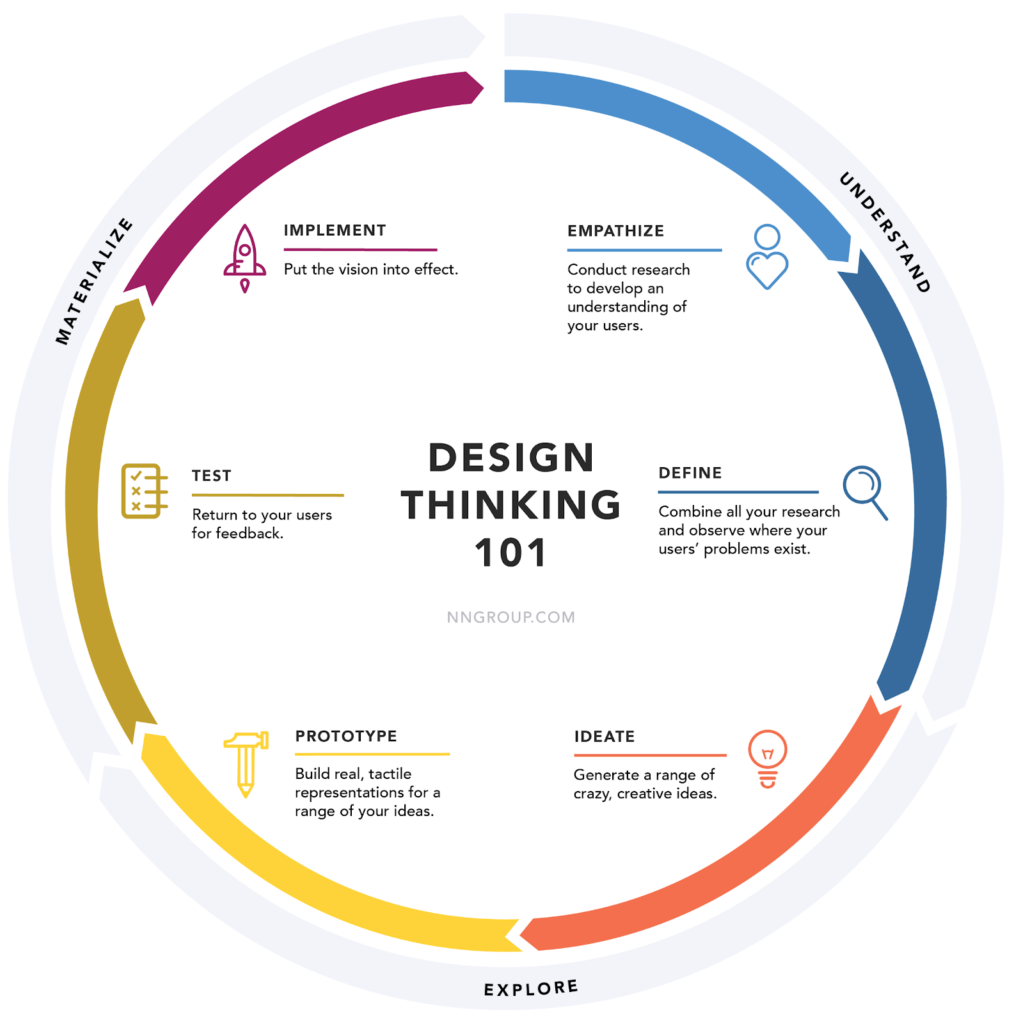
Design thinking has clearly defined stages and follows a logical order, but it is not actually a linear process. What is design thinking, if not a linear approach? Well, it is flexible and non-linear. After each stage of discovery in the design thinking process, you will need to go back to the previous stages and evaluate the steps taken.
What Is the Purpose of Design Thinking?
By now, you must be able to answer the question, “What is design thinking?” However, it is equally important to understand the purpose of the design thinking process. Whether it is business, education, or even a social cause, design thinking is an extremely powerful and useful approach. One of its most significant benefits is that it encourages creativity and innovation. It aims at using alternative solutions to solve our problems.
Often known as the healthy middle ground of problem-solving, design thinking is the perfect balance between giving in to emotion and intuition and depending on analytics and insights based on the scientific basis of measurement. It mixes a little bit of both.
But the core advantage of using design thinking to solve problems is that it places the human in the problem first. It puts human needs first. Since its focus is largely on the aspect of empathy, design thinking guides businesses to place primary importance on the experience of the customers. Better customer experience can only be achieved by providing customers with products and services that actually solve their problems.
What Are the Benefits of Design Thinking?
Design thinking is a crucial aspect of the product design process. A designer plays an important role in shaping the user experience. Think of a designer as the actual face behind the products and services that a brand creates and sells. It is your effort and talent as a designer that keeps a specific product or service in the market.
With the added tool of design thinking, you will be able to understand the users better. This can help you design products and services that are closely relevant for the users and also feasible, as per the resources and budget the company has.
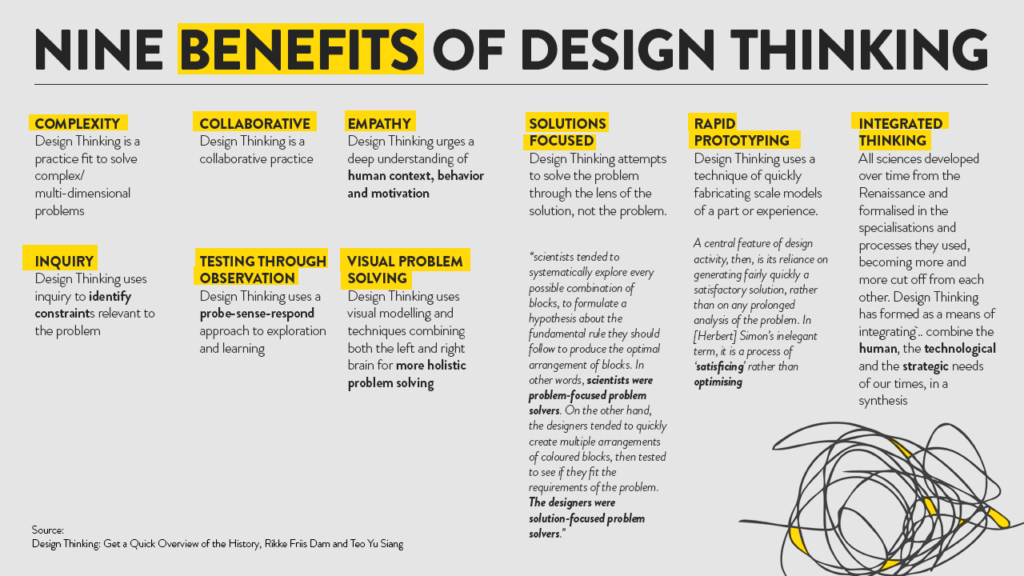
Now that you have understood the purpose of the design thinking methodology, here are some benefits this process has to offer:
1. It reduces time to market
By giving more importance to problem-solving via viable solutions, design thinking saves a lot of time that is usually spent on design and development. It significantly reduces production timelines, thereby expediting the development process.
2. It saves cost
By getting successful products to the market much faster, it is extremely beneficial in terms of cost savings. Design thinking also involves coming up with creative solutions that don’t weigh too heavy on the pocket.
3. It leads to better ROI
Design thinking has proven results in terms of yielding a higher ROI. Studies say that a sound design thinking process can fetch you up to 107% ROI.
4. It encourages customer retention
Design thinking also leads to an increase in customer retention, as the major focus of design thinking is enhancing the users’ experience. This results in better engagement on the users’ end, enabling long-term customer retention.
5. It is fuelled by innovation
Since the very idea of design thinking challenges assumptions, it encourages an out-of-the-box mindset. This fosters a culture that highly respects and appreciates innovation.
6. It has universal applications
Design thinking as a process is not just restricted to designers. It can be leveraged for cross-team collaboration and can be applied to literally any team within the company.
The Design Thinking Methodology in Action: An IBM Case Study
To help you understand design thinking in action, we will try to explain it in the form of a business case study. IBM is an excellent specimen of tapping into the potential of design thinking. It created an entire design thinking program as a part of its strategy.
Since the entire concept of design thinking is a complex idea to be explained and put to use straight away, IBM devised a few core practices that would make it easier to implement design thinking at work. The company leveraged design thinking to derive better client value, reduce overheads, and improve productivity, among many other goals. In order to do this, IBM had in place three techniques, collectively known as The Keys. Let’s explore each of them below.
1. Playbacks
The IBM design team realized that the only way to eliminate the redundancy that hierarchy brings is by creating a safe work environment, wherein individuals’ opinions and ideas can be discussed. There was a timeframe dedicated to the discussion of concepts and ideas, and then they were critiqued appropriately. This resulted in the establishment of a constructive critique environment and encouragement for brainstorming ideas.
2. Hill
A Hill is an important part of IBM’s design thinking toolkit. It refers to a statement of intent. What we usually come across as a point of view in generic design thinking has been translated to “Hill” by IBM’s design team. To be more specific, Hills are nothing but clear statements that tell the entire team what exact job has to be done. It helps center the product on the value it serves and problems it serves, tuning out other inessential elements. This creates micro-missions in a way and fosters effective team alignment.
3. Sponsor users
Sponsor users are basically people chosen from amongst the paying clients that are signed to co-design with the IBM design team. These people not only represent the problems and help the design team to understand issues more clearly, but they are also an important asset when it comes to validating discussed solutions. They add to the design team’s field research and help it in creating accurate buyer personas. The idea of collecting insights from clients is one of the most brilliant aspects of IBM’s design thinking methodology.
IBM’s Hallmark Program is an example of its design thinking strategy put to effect. While initially, IBM was reluctant to step into the realm of design thinking, now it has implemented design thinking concepts for many of its key business units, which include IBM security, IBM’s data, and artificial intelligence (AI) business, IBM’s digital strategies, and more.
Design thinking is now an integral aspect of IBM’s processes as well as product development teams. Here are a few of the many results it managed to achieve.
- 75% reduction in design time
- 33% reduction in development time
- 2X increase in time to market
- $18.6 million of increased profits
What Is the Relationship Between Design Thinking And UX Design?
Design thinking and UX design are both extremely user-centric processes. Another commonality between the two is that they are driven by the empathy factor. Both the processes also share a number of similar steps. But there are yet some clear differences between the two.
Design thinking tends to have a more strategic impact. It is adopted as an approach on a company-wide basis. UX design, on the other hand, focuses on ensuring the solutions so designed are usable, accessible, and are liked by the customers. To put it in a simpler way, design thinking is the methodology that designers need to create user experiences. It is, in a way, one of the many toolkits for UX designers.
How Can You Apply Design Thinking at Work?
The design thinking methodology, if applied to your work, can greatly enhance your efforts and maximize your ideas to perform excellently. It is one of those methods that will actually save your time while integrating the end user’s needs. In order to inculcate design thinking in your work and reap benefits from it, here are four steps you need to follow.
1. Focus on the problem
The major reason a number of companies fail at solving problems is that they primarily fail at understanding the problem. In order to identify the problem correctly, put yourself in the user’s shoes and approach the problem as they would. Think through them. Ask questions and engage with more than just your own team. Do not create rigid biases and assumptions.
2. Develop design thinking skills
Design thinking is not restricted to being used just by project managers and designers. Encourage everyone on the team to participate and brainstorm ideas, provide suggestions, etc. Gather feedback through testimonials and surveys, think of ways to test a new method, try to understand the user’s mentality in unique ways, and encourage your team members to experiment.
3. Conduct debriefs
One of the essential rules about the design thinking methodology is that it requires going back to the previous stages of the process after a new discovery. This process of iterating on previous stages can improve outcomes tremendously. Discuss what discoveries are useful and what could have been done better in the previous stages.
Ensure that failure is treated normally; it should not be taken as a setback. In fact, view failure as learning. Think of it as if it is a process of elimination that is only leading you closer to the best possible approach.
4. Embrace feedback
Design thinking does not deem perfection as its end result. It is rather aimed at learning as its goal. Implement a feedback loop. Test your assumptions in as many ways as possible. Iterate whenever there is an opportunity to do so. Conduct frequent feedback sessions. Create a safe space where mistakes can be discussed, and positive lessons can be learned from them.
Key Takeaways
- Design thinking is aimed at helping businesses solve complex problems in a highly user-centric manner. It places extreme emphasis on the needs and problems of the users.
- While design thinking has clearly defined stages, it is a flexible and non-linear approach.
- The primary focus of design thinking is placing humans first. It encourages businesses to constantly enhance user experience.
- Design thinking leads to increased customer retention and better ROI, and encourages innovation.
- Design thinking, as a process, is not just restricted to designers. It can be leveraged for cross-team collaboration, and can be applied to literally any team within the company.
- An excellent example of design thinking in action is IBM, which leveraged the former as an approach to rebuild customer trust and become a more relevant brand.
- Adopting the design thinking approach proved to be a huge learning curve for IBM. They received the insights they needed to increase product value as well as profits.
- Design thinking can be adopted as an approach on a company-wide basis. UX design, on the other hand, focuses on designing solutions and ensuring that they are usable, accessible, and are liked by the customers.
- The design thinking methodology, if applied to your work, can greatly enhance your efforts and maximize your ideas to perform excellently.
- In order to identify the problem correctly, put yourself in the user’s shoes and approach the problem like they would.
- One of the essential rules about the design thinking methodology is that it requires going back to the previous stages of the process after any new discovery.
Conclusion
So, what is design thinking? It is a great way of identifying and solving the problems in an organization, at not only an individual- or team-level, but also at a company-wide level. Inspiration, ideation, and implementation are the major elements of design thinking; and by striking the right balance between the three, you can be a skilled design thinking leader. But it is equally important to test the ideas generated through the design thinking process and gauge their efficacy.

FAQs
As per the Design Council of the UK, the four Ds of design thinking include discovering, define, develop, and deliver.
The stages of design thinking are as follows.
Research the users’ needs.
Define the users’ needs and problems.
Challenge assumptions.
Brainstorm and ideate.
Develop solutions.
Test your solutions.
Gather feedback and work towards improving your solutions.
A design thinking leader knows how to act as a catalyst for creativity. As a design thinking leader, an individual needs to know the process of problem-solving thoroughly.
Design thinking is essential as it helps you observe and develop empathy with the target customer. This further enables you to address the problems, assumptions, and implications as well.
A design metric is a quantitative measurement that verifies the quality of a design. It helps measure the implementation of features, such as cost, size, power, and performance, among others.
Designing for impact is aimed at using the application of design to enable better customer outcomes.
Latest Blogs
Explore how Google’s 2025 AI search updates triggered ranking chaos. Learn actionable strategies to adapt your SEO for AI Overviews, zero-click searches, and SERP volatility. Stay ahead now.
Learn how to rank on AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini by optimizing your content for authority, structure, and relevance. Stay ahead in AI-driven search with this strategic guide.
Explore the best healthcare SEO services for your medical practice. Improve online visibility and effectively reach more patients in need of your services.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Design
7 mins read
15 Best Firms Offering Design Services in India

Design
5 mins read
All You Need to Know About Data-Driven Design

Design
6 mins read