UI/UX Design: Its Importance and Differences

Table of Contents
- What is UI UX Design?
- How UI Design and UX Design Complement Each Other
- The Differences Between UI Design and UX Design
- UI Design and UX Design: Best Practices for Websites
- Checklists for Superior UI Design and UX Design
- Key Takeaways
- Conclusion: The Future of UX and UI
- FAQs
“This product has a great UX.” “That app has a superb UI.” When people make such statements, what are they referring to? That’s what we’re going to explore in some detail. We’ll answer the question: what is UI UX design? How do they differ from each other, and what is their importance for customer retention and loyalty?

What is UI UX Design?
UX design stands for User Experience design. It’s involved with how human beings interact with products and services. It ranges from digital products such as websites and apps to everyday appliances like phones and toasters.
UX isn’t a new process. For decades, engineers and product designers have examined this issue to make design improvements. Nowadays, there is an even greater emphasis on the human factor.
The term UX was coined by Donald Norman, who was working with Apple as a user experience architect. He used it to cover all aspects of experience with a system. This included industrial design, graphics, software interface, physical interaction, and even the user manual.

An emphasis on UX design reduces bugs in the final version. It results in reduced costs and products that are pleasing to use. This leads to boosted conversions as well as customer loyalty.
On the other hand, UI design stands for User Interface design. This refers to the look and style of digital applications. It includes the clickable buttons, layout, animations, drop-down menus, and every other graphic element the user interacts with. The aim is to make the process seamless, intuitive, and pleasing.
When done well, UI design eliminates customer pain points and enhances stickiness. If an interface is aesthetically satisfying and functionally simple, it draws consumers in and keeps them there. In this way, UI design is important to increase loyalty and create a competitive advantage.
How UI and UX Design Complement Each Other
As we’ve seen, UX and UI are different disciplines. However, they work hand-in-hand to enhance consumer appeal. UX design makes interactions fulfilling and UI design makes the experience satisfying. UX is goal-oriented and UI takes this a step further to involve consumer emotions.
UX Design
Another way to look at it is that UX designers optimize product use and UI designers work to make the process simpler. An understanding of how UX and UI designers perform their tasks shows how the two disciplines are linked.
UX design starts with the client’s brief. This is followed by research and observation. Users provide information on the way they use products, their pain points, and their expectations. This is essential for UX designers to understand product usage in a real-world scenario.
Then comes the actual design process. UX designers create a series of wireframes and prototypes. Experiments are conducted and modifications are carried out. Usability and functionality are assessed at all levels.
The final prototypes are then tested. Feedback is gathered so that problems can be identified and corrections can be made. Testing is an important step in the UX design process, as it saves cost and time.
UI Design
In UI design, the process starts with collaboration. Inputs have to be taken from UX designers and others from the team. This makes the designers understand the role of the final product and the types of end-consumers.
After this, UI designers create an overall look and feel for the interface. Interactivity and consistency are important yardsticks. A distinctive brand identity is often the desired element.
When it comes to the implementation of the design, the UI team has to consider responsiveness, formats, type size, and several other elements. The consumer’s perspective has to be considered at each step. Typically, workflows are created to understand this.
In this way, the work of UX and UI teams is linked for superior usability and design. Both have to achieve their objectives in tandem to create a stellar experience for the consumer.
The Differences Between UI Design and UX Design
With the above information, we get a clearer answer to the question of what UX design is, and its differences with UI design. UX design is a factor throughout products, interfaces, and services. UI design has to do with interfaces. Here are some other points of difference.
- UX has to do with the functionality of the product in use. With UI, the focus is on the way the consumer interacts with the product.
- UX starts with market research, spotting consumer needs, and providing value. With UI, there are aesthetic choices to do with the look, feel, and responsiveness.
- UX starts from the first step of product development: the idea and the prototypes. With UI, attention is paid to the way the finished product looks.
- UX design often starts with listening to the client’s needs and requirements. UI designers focus on the consumer’s expectations.
- UX design is concerned with all types of interactions between the customer and the brand. This is to do with specific products as well as aspects such as service and feedback. UI design is focused on providing a visual interface that communicates the benefits and advantages of the digital product.
UI Design and UX Design: Best Practices for Websites
When it comes to websites, the functions of UI and UX design are even more closely linked. That is why both are sometimes used interchangeably. Here are some best practices for UX design in websites:
- A design that is pleasing to look at but does not overload resources.
- Distinctive page icons that are not distracting.
- Establishing an online hierarchy and making it simple to navigate across pages.
- Drawing attention to important sections such as the call to action.
- Providing background differentiation between sections while adhering to the overall brand identity.
These are some best practices for UI design in websites:
- Displaying only relevant and actionable information on each screen.
- Ensuring consistency across elements.
- Using a color palette that reflects the intent of the website and brand.
- Ensuring that the flow between elements is seamless and in line with the user’s journey.
Checklists for Superior UI Design and UX Design

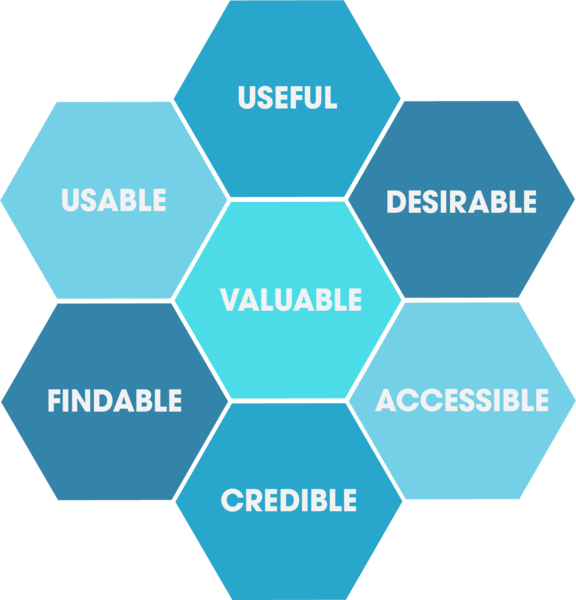
Memorable UI and UX design are made up of many elements. Many designers refer to a “usability honeycomb” to understand all of them. They also use checklists. This ensures that design functionality and appeal are not compromised. Here are some of the main elements in such checklists.
UX Design Checklist
- Competition and data analysis. The product offering should be unique and in line with consumer needs.
- User feedback. Research insights on consumer interaction and pain points should be taken into account.
- Flow. The consumer’s eye should be seamlessly guided towards relevant elements of the screen.
- Responsiveness. At all stages of consumer interaction, the product should be engineered to deliver an appropriate and speedy response.
- Prototypes and Wireframes. The first iterations of the product should be tested for problems and revisions.
- A/B test plans. Sometimes, there can be two versions to be tested. The one that receives better feedback is to be taken ahead.
- Final tests and corrections. Based on further consumer interactions, appropriate feedback is to be incorporated. Final checks are to be implemented.
UI Design Checklist
- Typography. The text should be legible against various backgrounds. Too many font styles should not be used.
- Style. If there is an existing brand guideline, this should be adhered to. The design should not look different from other brand offerings.
- Adaptability. Depending on the type of consumer and usage pattern, the design should be adaptable across platforms and screen sizes.
- Compliance. Often, there are standards to be met regarding specific devices and platforms, such as those from Google and Apple.
- Functionality. All elements should function properly, including background scripts, buttons, and other settings.

Key Takeaways
- Though UI and UX design are sometimes used interchangeably, there are differences between them.
- UX design is User Experience design, which is applied to how human beings interact with products and services.
- UI design is User Interface design, which refers to the look and style of digital applications.
- UX design leads to products that provide high satisfaction in use, leading to conversions and loyalty. This means boosted conversions as well as customer loyalty. UI design removes pain points and enhances stickiness. Both provide a competitive advantage.
- The roles of both are complementary. UX design makes interfaces intuitive, and UI takes this a step further to provide functional aesthetics. When UI design and UX design teams work together, it results in superior usability and design.
- UX design starts with the client’s requirements. UI designers focus on the consumer’s expectations.
- UX design is present in products, interfaces, and services. UI Design is targeted at interfaces.
- Both UI and UX designers rely on checklists to ensure a superior product. For UX, checklists include data analysis, responsiveness, and prototypes. For UI, the points are typography, compliance, and style.
Conclusion: The Future of UX and UI
UI design and UX design are continually evolving disciplines. Changes in technology, customer channels, and product offerings are driving new applications and functionalities.
For example, with the rise of virtual reality and augmented reality, the answer to the question “what is UI UX design” will have to include relevant 3D interfaces and the use of gestures.
Both UI design and UX design will remain critical disciplines for product development. The importance of simplicity, seamlessness, and responsiveness will increase with a new generation of products.
In time, UI/UX designing will become even more integrated into production processes. As Steve Jobs once said: “Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.”
FAQs
UI and UX are connected practices. UX is to do with a consumer’s overall experience with a product and UI is involved with consumer interfaces.
UI/UX design makes the end user’s interaction with a product satisfying and seamless. UI/UX developers understand consumers’ expectations, remove pain points, and increase loyalty and usage.
UI refers to the user interface, whereas UX refers to the user experience.
With UI, the emphasis is on creating design elements that are accessible, robust, and functional. With UX, the focus is on understanding all consumer touchpoints with a product and making the experience harmonious and satisfying.
Coding is not an essential skill in UI and UX design. However, those who know how to code have an advantage. It can expand job opportunities, help in understanding product possibilities, and facilitate better communication.
Latest Blogs
Explore how Google’s 2025 AI search updates triggered ranking chaos. Learn actionable strategies to adapt your SEO for AI Overviews, zero-click searches, and SERP volatility. Stay ahead now.
Learn how to rank on AI search engines like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini by optimizing your content for authority, structure, and relevance. Stay ahead in AI-driven search with this strategic guide.
Explore the best healthcare SEO services for your medical practice. Improve online visibility and effectively reach more patients in need of your services.
Get your hands on the latest news!
Similar Posts

Design
7 mins read
15 Best Firms Offering Design Services in India

Design
5 mins read
All You Need to Know About Data-Driven Design

Design
6 mins read